The Abaqus 2024 release introduces several noteworthy features and enhancements across different modules, enhancing its capabilities for structural and thermal simulations. Here’s a concise overview of key updates:
ABAQUS/CAE
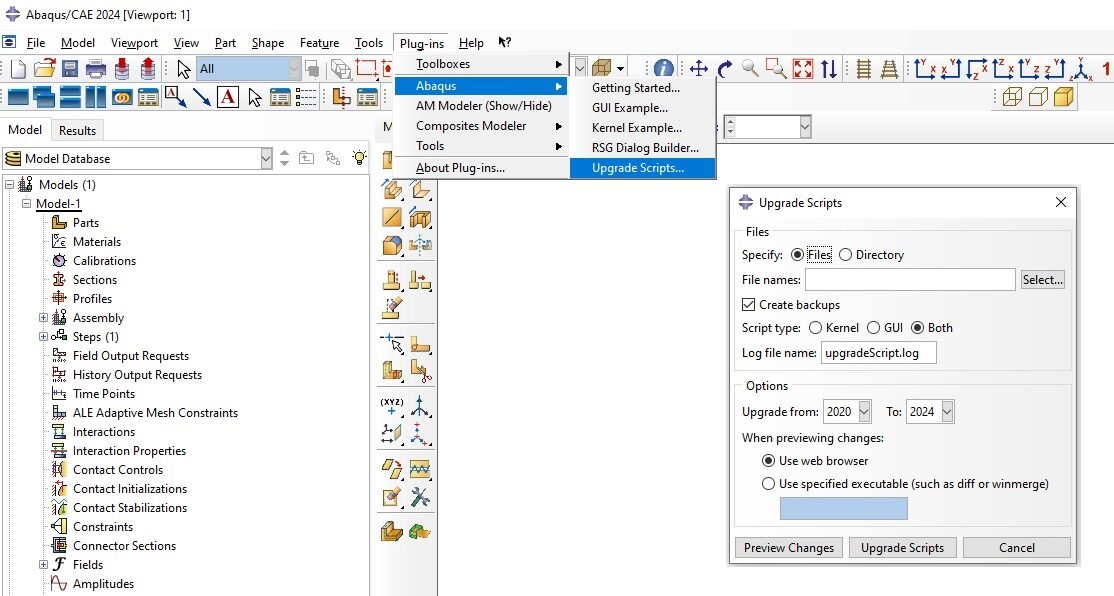
- Transition to Python 3: In the Abaqus 2024 release, there is a significant update as Abaqus Python and Abaqus/CAE transition to Python 3.10, aligning with the latest open-source community standards. This transition promises a more streamlined and secure scripting experience. However, it’s crucial to note that this transition may present challenges, especially concerning existing plug-ins that might not seamlessly integrate with Python 3.10. To navigate this, users are advised to be cautious during the transition phase and consider potential adjustments to their scripts.A helpful tool in this process is the Upgrade Scripts tool in Abaqus/CAE (see image below), which assists in the conversion of Python 2 code to Python 3. After preparation, testing becomes paramount to ensure that scripts continue to function as expected.
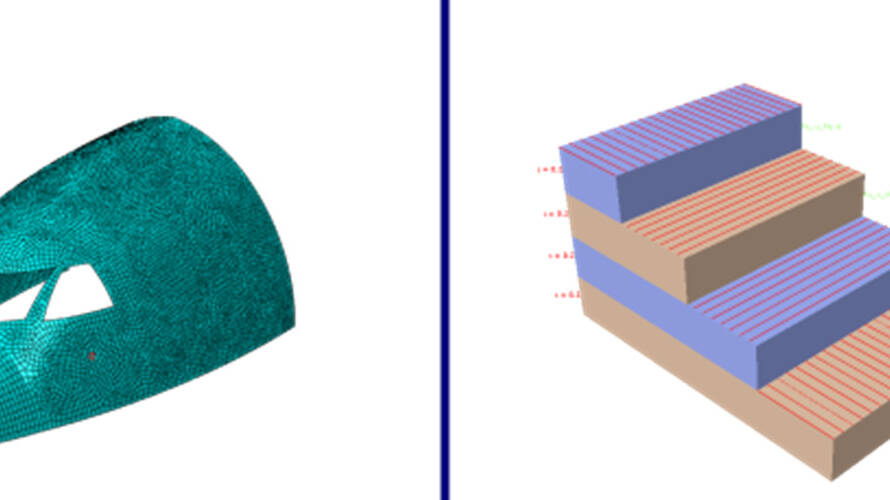
- Render Styles in Plots for Continuum Particle Elements: Users can now visualize element particle edges using various render styles such as wireframe, hidden, filled, and shaded. These options are accessible through the (View ODB Display Options) menu. This enhancement offers users the flexibility to assign different render styles, providing an improved visual experience.
- Step-Dependent General Contact (Abaqus 2024 FD01): Abaqus/CAE now supports general contact definition in any analysis step, enabling more complex contact behaviors.
- Contact Mass Scaling: Abaqus/CAE now supports contact mass scaling in Abaqus/Explicit. This improvement offers the advantage of reducing the required increments for simulations using non-default penalty stiffness in Abaqus/Explicit. Contact mass scaling can be applied selectively to the contact surfaces or elements involved in the contact definition. Its implementation helps mitigate the impact of elevated contact penalty stiffness on the global stable time increment in Abaqus/Explicit analyses by adjusting the mass associated with the contact surfaces, leading to enhanced simulation efficiency.
- Channel and Hat Section Profiles: Enhanced Property module to define channel and hat section profiles for beam cross-sections.
- Rotational Couplings: Introduction of rotational coupling type in discrete fasteners and coupling constraints for improved control.
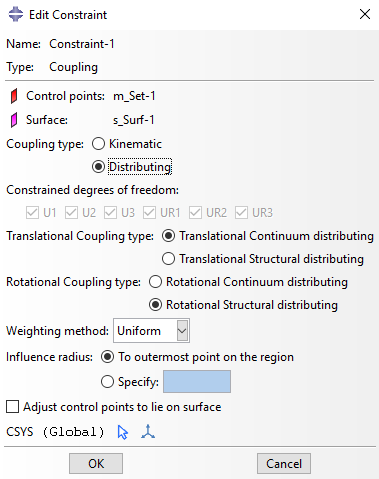
- Linearized Contact Capability: Activation of linearized contact capability in Abaqus/CAE to solve contact status and contact stresses within a static perturbation step with small-sliding, frictionless contact. Faster solutions in certain classes of contact problems.
Analysis
- Formation of Tie Constraints in Import Analysis: When transferring results between Abaqus analyses, the functionality of tie constraint formation during import analysis in Abaqus/Explicit proves highly beneficial. Now, tie constraints are established using the original configuration, ensuring consistency if both main and secondary surfaces remain unchanged from the original analysis. This not only simplifies the establishment of initial equilibrium in the imported model but also prevents the creation of new tie constraints for nodes on surfaces previously untied. Such prevention is crucial to maintaining the imported model’s consistency, especially when dealing with nodes in a contact state. Furthermore, this updated protocol ensures the consistent establishment of identical tie constraints for surfaces in the import analysis, maintaining uniformity with the original analysis. This remains applicable irrespective of whether the reference configuration for import is specified as the original or the updated configuration.
- Adjoint Sensitivity Analysis for Sizing Optimization: New capabilities for computing adjoint sensitivities in direct steady-state dynamic analysis, facilitating sizing optimization. We can now optimize for the steady-state response (direct-solution) of a structure subjected to harmonic excitations.
KEYWORDS
- *New NODE RESPONSE RANGE OPERATOR Parameter: Enables control over the calculation of design responses over a frequency range in steady-state dynamic adjoint sensitivity analysis.
OUTPUT
New Output Variables: Introduction of new output variables such as
- STIFN: Local normal stiffness.
- VN: Complex-valued surface normal velocity.
- NSQ: Real-valued surface normal velocity squared.
- AVNSQ: Area-weighted surface normal velocity squared, or acoustic power normalized by the acoustic impedance of the surrounding fluid.
- FEXT: All components of external point loads from a co-simulation or external field definition.
- MEXT: All components of external point moments from a co-simulation or external field definition.
- DISP_NORMAL_VAL: The value of the bead optimization displacement along the node normal vector.
These updates collectively enhance Abaqus 2024, providing users with improved functionality, visualization options, and flexibility in simulating a wide range of structural and thermal scenarios. For more detailed information, refer to the Abaqus Release Notes in the 2024 SIMULIA User Assistance.
This blog will be automatically updated with the new enhancements from the hotfixes. Register to get notice when it updates!